In my recent evaluation of home internet connectivity, I explored the contrasting dynamics of Wi-Fi and Ethernet, revealing critical insights that may influence your choice between these two options. While Wi-Fi provides undeniable convenience, its performance can be unpredictable due to environmental factors. Conversely, Ethernet consistently offers enhanced stability and lower latency, particularly beneficial for activities requiring high bandwidth. This analysis raises pertinent questions about what truly matters in our increasingly connected lives—ease of use or reliability? The implications of these findings warrant further exploration for anyone seeking ideal internet performance.
My Home Internet Experiment
In my home internet experiment, I meticulously tested the performance of both Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections to uncover surprising disparities in speed and reliability.
My findings revealed that Wi-Fi consistently achieved speeds averaging around 250 Mbps, considerably outperforming Ethernet, which measured under 100 Mbps.
This disparity prompted a deeper investigation into the pros and cons of each connection type. Factors such as network settings, the integrity of Ethernet cables, and the specifications of Ethernet adapters played vital roles in determining internet speed.
Remarkably, LAN transfers to a home server exhibited variability in Ethernet performance, underscoring that a direct connection does not always guarantee superior speeds.
Understanding these nuances is essential for optimizing network performance in various setups.
Understanding Wi-Fi
Understanding the intricacies of Wi-Fi technology is essential for optimizing wireless connectivity and ensuring reliable internet access across multiple devices.
Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, allows devices to connect to a wireless network without physical cables, offering speeds ranging from 25 Mbps to 1 Gbps.
However, the performance of a Wi-Fi connection can be influenced by environmental factors such as distance and obstacles, which may lead to interference that degrades signal quality.
While Wi-Fi provides the advantage of convenience and flexibility, it also has disadvantages, including potential congestion from multiple devices sharing bandwidth.
To enhance performance, strategically positioning the router can markedly improve signal strength and reduce dead zones, thereby maximizing the benefits of a Wi-Fi network.
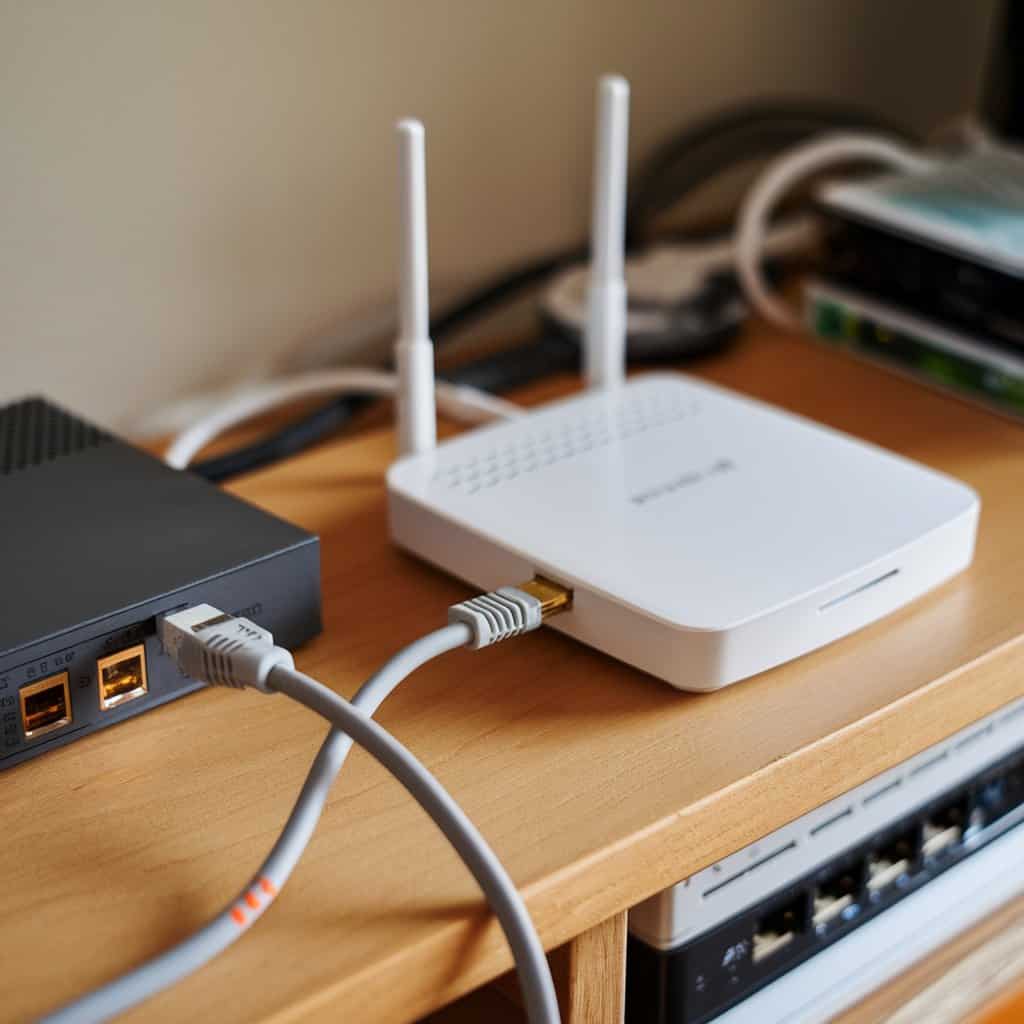
Understanding Ethernet
Ethernet technology delivers a reliable wired connection that typically surpasses wireless options in terms of speed and stability. This network connection is essential for users who prioritize consistent performance.
Here are three key aspects of wired Ethernet:
- Types of Ethernet: Common types include CAT5, CAT5E, and CAT6, each supporting various bandwidths and distances.
- Reduced Interference: Wired Ethernet connections are less prone to interference, leading to lower latency and enhanced reliability for data transfer.
- Security Benefits: Ethernet provides a more secure environment, as physical access to the network is required to intercept data, making it harder for unauthorized users to access the internet.
Performance Comparison
A performance comparison between Wi-Fi and Ethernet reveals significant differences in speed, latency, and reliability, impacting users’ overall internet experience.
Ethernet connections typically achieve speeds up to 395 Mbps, while Wi-Fi averages around 126 Mbps.
Latency is another critical factor; Ethernet maintains levels under 10 ms, making it ideal for gaming consoles and real-time applications, whereas Wi-Fi latency ranges from 20-50 ms.
Distance and physical barriers can degrade Wi-Fi performance, unlike Ethernet, which offers consistent speeds over distances of up to 100 meters.
Furthermore, modern Ethernet standards can reach data transfer rates of up to 10 Gbps, surpassing Wi-Fi’s maximum of 1 Gbps.
Ultimately, for demanding internet connections, Ethernet often outperforms Wi-Fi, especially in fiber optic setups.
Cost Analysis
How do the initial and long-term costs of Wi-Fi and Ethernet compare when considering the overall investment in a home network? A thorough cost analysis reveals distinct financial implications for both options:
- Installation Cost: Ethernet often incurs higher upfront expenses due to specialized ethernet cables and potential labor for installation, whereas a basic Wi-Fi router is typically less costly and easier to set up.
- Maintenance Costs: Wi-Fi networks may require periodic upgrades and additional equipment like extenders, which can add to long-term expenses.
- Budget Constraints: Homeowners must weigh initial investments against future upgrade needs, making extensive cost evaluations critical to align with budget constraints.
Ultimately, understanding these financial factors is essential for making an informed decision regarding home networking solutions.
Security Considerations
Security considerations play an essential role in choosing between Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections, as each presents distinct vulnerabilities and protective measures.
Ethernet cables provide enhanced security due to their physical nature, requiring direct access to intercept data, thereby reducing unauthorized access risks.
In contrast, Wi-Fi networks are more susceptible to attacks like eavesdropping, particularly in densely populated areas.
Implementing strong encryption protocols, such as WPA3, along with robust passwords, is critical to safeguard Wi-Fi networks. Regularly updating router firmware also bolsters security.
Additionally, utilizing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can further protect both Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections by encrypting internet data during transmission, adding an essential layer of security against potential breaches.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, the choice between Wi-Fi and Ethernet hinges on individual needs and preferences, balancing factors such as speed, stability, and mobility in the context of specific internet usage scenarios.
For those seeking the best home internet experience, consider the following:
- Speed Requirements: If you need much faster connections for tasks like gaming or 4K streaming, Ethernet may be the better option.
- Mobility Needs: If you prefer flexibility and the ability to connect multiple devices without physical constraints, Wi-Fi offers significant advantages.
- Connection Stability: For activities that require consistent performance, such as video conferencing, being connected directly via Ethernet will generally yield better results.
In the debate between Wi-Fi and Ethernet, several factors emerge as essential, including speed, stability, and flexibility.
While Wi-Fi offers convenience, its performance can be inconsistent due to environmental influences.
Conversely, Ethernet provides a reliable connection, particularly beneficial for activities requiring low latency, such as gaming and streaming.
Ultimately, the choice hinges on individual preferences and specific needs.
In the end, it becomes clear that one must weigh the pros and cons carefully to avoid a rocky road ahead.